Technical SEO Basics Every Web Designer Should Know

When it comes to building a successful website, good design is important but it’s not everything. A beautiful site that loads slowly or is hard for search engines to crawl won’t perform well in Google search results. That’s where Technical SEO comes in.
If you’re a web designer, you don’t need to be an SEO expert, but understanding the basics of technical SEO will help you create websites that not only look good but also perform well in search engines.

In this blog, we’ll break down the core technical SEO elements every web designer should know in plain, simple English.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the part of SEO that focuses on making a website easier for search engines like Google to crawl, index, and rank.
It deals with:
- How fast your website loads
- How easy it is for Google to read your content
- Whether your website works well on mobile
- If your site has broken links or errors
- And more…
Think of it like this:
If content is the “voice” of your website, technical SEO is the “engine” that makes everything run smoothly behind the scenes.
Why Should Web Designers Care About Technical SEO?
As a designer, you build the structure of the website. And if that structure has issues like being too slow or hard to navigate no amount of content can fix that.
Here’s why technical SEO matters to you:
- Better structure = better crawlability by Google
- Faster websites = better user experience = higher rankings
- Clean code = fewer issues for SEO experts to fix later
- Good mobile design = better performance in mobile-first indexing
Now, let’s get into the key areas of technical SEO you should know.
1. Website Speed (Page Load Time)
Why Speed Matters:
Google has said page speed is a ranking factor. A slow-loading website not only frustrates users but also affects your visibility in search results.
What You Can Do:
- Use lightweight themes and frameworks. Avoid bloated templates that slow things down.
- Compress images before uploading. Use tools like TinyPNG or WebP formats.
- Enable lazy loading for images so they only load when the user scrolls.
- Minimize CSS and JavaScript files. Remove unused code and combine files where possible.
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to serve files from the closest server.
Tools to Check Speed:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- GTmetrix
- WebPageTest
2. Mobile-Friendliness
Why It Matters:
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it looks at your site’s mobile version first to decide how to rank it.
What to Do:
- Use responsive design. Your website should adapt to all screen sizes phones, tablets, desktops.
- Avoid popups that cover content on mobile.
- Use readable font sizes and clear CTAs (call-to-actions).
- Ensure navigation is easy on small screens.
You can test your site using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
3. Clean, Crawlable Code
Why This Matters:
Search engine bots “crawl” your site by reading its code. Clean and semantic HTML makes this easier.
Best Practices:
- Use proper HTML tags (e.g., <header>, <main>, <footer>, <article>).
- Avoid inline styles and excessive JavaScript.
- Minimize use of iframes unless absolutely necessary.
- Use canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues.
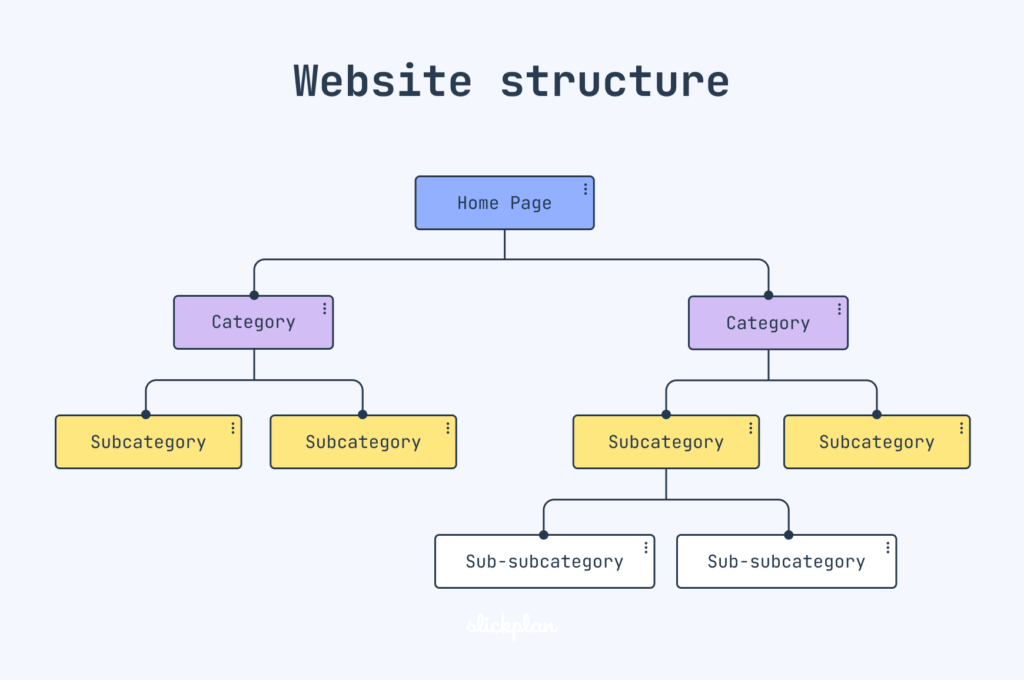
4. Website Architecture and URL Structure
What Is Website Architecture?
It’s how your site is organized how pages link to each other and how easy it is to find important pages.
What to Keep in Mind:
- Use a flat architecture. Try to keep every page reachable within 3 clicks from the homepage.
- Create logical internal linking. For example, link your blog posts to relevant service pages.
- Use SEO-friendly URLs:
- Good: yourdomain.com/seo-services
- Bad: yourdomain.com/page?id=1234
- Good: yourdomain.com/seo-services
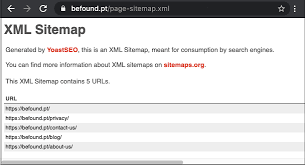
5. XML Sitemap and Robots.txt
What’s an XML Sitemap?
A sitemap tells search engines which pages exist on your site and helps them crawl those pages.
What’s Robots.txt?
This is a file that tells search engines which parts of your site not to crawl.
Best Practices:
- Add an XML sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console.
- Create a proper robots.txt file (don’t accidentally block important pages!).
- Use noindex meta tags to hide pages you don’t want in Google (like admin pages or thank-you pages).
6. HTTPS and Secure Websites
Why HTTPS Matters:
Google gives a ranking boost to secure websites. Users also trust sites with a padlock symbol.

Action Steps:
- Always use SSL (Secure Socket Layer).
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS using 301 redirects.
- Make sure all internal links point to HTTPS URLs (not HTTP).
You can get free SSL certificates from Let’s Encrypt.
7. Core Web Vitals (User Experience Metrics)
Google introduced Core Web Vitals as a ranking factor. These are metrics that measure real-world user experience.
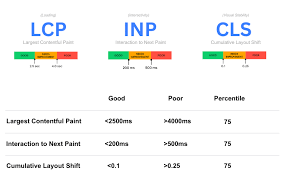
Core Metrics:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) – How fast the main content loads
- FID (First Input Delay) – How fast the site responds to user actions
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) – How stable the layout is (no jumping elements)
How to Improve:
- Optimize images and fonts
- Remove render-blocking scripts
- Reserve space for ads/images to prevent layout shifts
Use Google Search Console or PageSpeed Insights to monitor these.
Also Read : What the Creator Economy Will Look Like in 2027
8. Structured Data (Schema Markup)
What Is Structured Data?
It’s code you add to your pages to help search engines understand your content better. It can also help your site appear with rich results (stars, FAQ dropdowns, etc.).

Examples:
- Product pages → Use Product schema
- Blogs → Use Article schema
- Events → Use Event schema
- Local businesses → Use LocalBusiness schema
Use tools like Schema.org and Google’s Rich Results Test.
9. Broken Links and 404 Errors
Why It Matters:
Broken links = bad user experience = negative SEO signals.
Fixes:
- Regularly scan your site with tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs.
- Use proper 301 redirects when you move or delete pages.
- Create a custom 404 page that helps users navigate elsewhere.
10. Image SEO for Better Rankings

Optimization Tips:
- Use descriptive file names (e.g., blue-wool-scarf.jpg)
- Add alt text to every image for accessibility and SEO
- Compress images to reduce load time
- Use WebP format for better compression
Search engines also index images optimized images can bring traffic from Google Image Search.
11. Avoiding Duplicate Content
❌ Duplicate Content Hurts SEO
When Google sees the same content in multiple places, it doesn’t know which to rank — so your visibility drops.
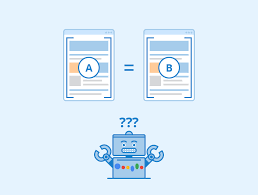
✅ Solutions:
- Use canonical tags to point to the preferred version of a page
- Don’t publish identical content across subdomains
- Avoid copying manufacturer descriptions or blog content from other sites
12. Use SEO Plugins (For CMS Sites Like WordPress)
If you’re designing WordPress sites, use plugins like:
- Rank Math
- Yoast SEO
- All in One SEO

These plugins help you:
- Generate sitemaps
- Set canonical URLs
- Add schema
- Control meta titles and descriptions
13. Indexing and Crawl Budget
What’s Crawl Budget?
It’s the number of pages Googlebot will crawl on your site in a given period.
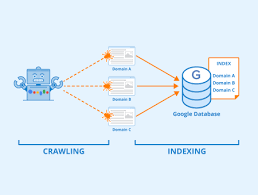
Keep Things Clean:
- Remove low-value or thin pages
- Block unnecessary pages with robots.txt
- Don’t overload your site with thousands of useless URLs (like filters, tag pages, etc.)
14. SEO-Friendly Navigation
Menus and internal navigation should be:
- Clear and easy to follow
- HTML-based instead of JavaScript-heavy
- Linked with anchor text that includes keywords (e.g., “SEO Services” instead of “Click here”)
Good navigation helps both users and search engines find pages easily.
15. Testing and Maintenance
Technical SEO isn’t a one-time task. As a web designer, you should:
- Test your site before launch
- Monitor regularly using Google Search Console
- Collaborate with SEO professionals to make changes
Summary: Quick Technical SEO Checklist for Web Designers
| SEO Element | What to Check |
| ✅ Page Speed | Compress images, reduce code, use CDN |
| ✅ Mobile-Friendly | Responsive design, good UX |
| ✅ Clean Code | Semantic HTML, fewer inline styles |
| ✅ URLs | SEO-friendly, short, meaningful |
| ✅ HTTPS | Secure with SSL |
| ✅ Sitemap | Submit XML sitemap to Google |
| ✅ Robots.txt | Don’t block important pages |
| ✅ Structured Data | Use schema for rich snippets |
| ✅ 404 Errors | Fix broken links, add custom 404 page |
| ✅ Core Web Vitals | Optimize for speed, interaction, stability |
| ✅ Image SEO | Use alt tags, compress, descriptive names |
| ✅ Duplicate Content | Use canonicals, avoid thin pages |
Final Thoughts: Web Designers + Technical SEO = Powerful Combo
As a web designer, your role is evolving. You’re not just creating beautiful websites—you’re building high-performing digital assets.
When you understand the basics of technical SEO:
- Your designs load faster
- Your sites rank better
- Clients are happier
- You stand out as a skilled professional
You don’t need to do everything yourself, but knowing what matters and how to avoid common mistakes can take your web design projects to the next level.