How to Conduct a Comprehensive SEO Audit for Your Website

If your website isn’t performing well in search engine rankings, an SEO audit is the first step to fixing the problem. A comprehensive SEO audit helps identify issues that could be holding back your website from achieving its full ranking potential.

In today’s digital world, search engines continuously update their algorithms. Without regular SEO audits, your site may become outdated, lose visibility, and fail to attract organic traffic. But don’t worry! This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about conducting an SEO audit like a pro.
What is an SEO Audit?
Definition and Purpose
An SEO audit is a detailed analysis of your website’s technical, on-page, and off-page SEO factors. The goal is to uncover weaknesses and opportunities for improvement that can help your site rank higher in search engines like Google.
When Should You Perform an SEO Audit?
SEO audits aren’t just for when your rankings drop! You should conduct an SEO audit:
- Quarterly or bi-annually to stay ahead of algorithm updates
- After launching a new website to ensure it’s optimized
- Before a major website redesign to avoid losing rankings
- If traffic or rankings suddenly decline to diagnose potential issues
Preparing for an SEO Audit
Tools You Need
Before you start, gather the right SEO tools. Some of the best ones include:
- Google Search Console : To check indexing, errors, and performance
- Google Analytics : For traffic insights and user behavior
- Ahrefs / SEMrush : To analyze backlinks and keyword rankings
- Screaming Frog : To conduct a full-site crawl
- PageSpeed Insights : To test website speed
Setting Clear Goals
Define what you want to achieve with the audit. Are you aiming to fix technical issues? Improve content strategy? Optimize backlinks? Having clear goals will help you prioritize tasks.
Technical SEO Audit
Checking Site Speed and Performance
Google prioritizes fast-loading websites. Use Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze your page speed and find opportunities for improvement.
Mobile-Friendliness and Responsiveness
Since Google follows mobile-first indexing, your site must be mobile-friendly. Run a Google Mobile-Friendly Test to see if your site performs well on smartphones.
Also Read: On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO: What’s the Difference?
Analyzing Site Structure and Crawlability
A well-structured site is easier for search engines to crawl. Make sure:
- Your site has an XML sitemap submitted in Google Search Console
- There are no broken links
- The robots.txt file isn’t blocking important pages
Fixing Broken Links and Redirect Issues
- Use Screaming Frog to detect 404 errors
- Implement 301 redirects where necessary
- Remove or replace broken internal and external links
On-Page SEO Audit
Analyzing Content Quality and Keyword Usage
Content is king Your pages should include high-quality, keyword-optimized content that satisfies user intent. Check for:
- Keyword stuffing (avoid it!)
- Missing or duplicate content
- Proper use of headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions should be compelling, keyword-rich, and within Google’s character limits.
Internal Linking Strategies
Use internal links to help users and search engines navigate your site. Each page should link to relevant content to boost SEO.
Off-Page SEO Audit
Evaluating Backlink Profile
Backlinks are a huge ranking factor. Use Ahrefs or SEMrush to analyze your backlink profile.
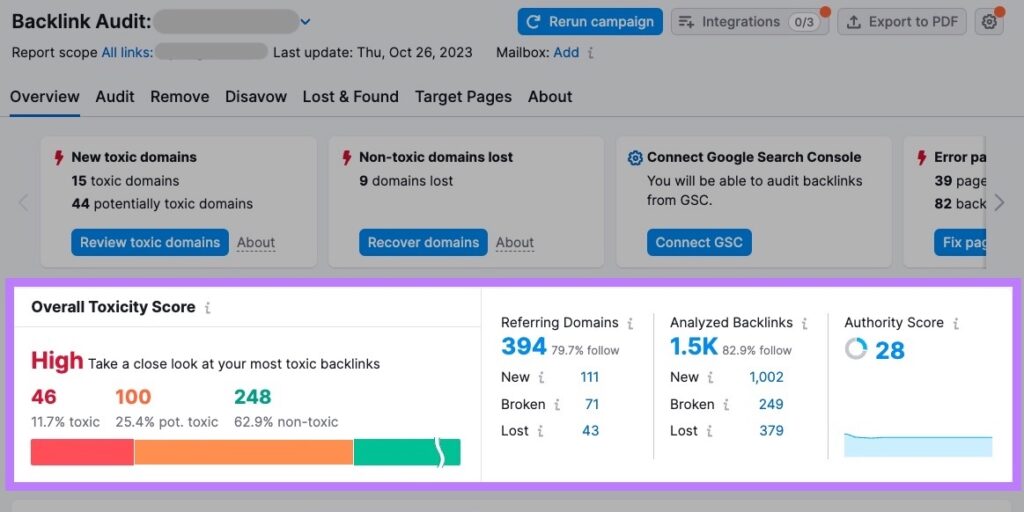
Identifying Toxic Backlinks
Toxic backlinks can hurt rankings. Disavow harmful links using Google’s Disavow Tool if needed.
Competitor Backlink Analysis
Check where your competitors get their backlinks and try to acquire similar ones.
Content Audit
Checking for Duplicate and Outdated Content
Duplicate content can lead to ranking issues. Use Siteliner to detect duplicates and refresh outdated posts.
Improving Content Relevance and Readability
- Use short paragraphs and bullet points
- Optimize for featured snippets
- Add high-quality images and videos
User Experience (UX) Audit
Page Layout and Navigation
User experience plays a significant role in SEO rankings. If visitors struggle to navigate your site, they will leave quickly, increasing your bounce rate which signals to search engines that your content isn’t valuable.
To improve UX:
- Ensure easy navigation with a clear menu structure
- Use breadcrumbs to help users find their way back
- Keep your design clean and uncluttered
Bounce Rate and Engagement Metrics
Check Google Analytics for bounce rate, session duration, and pages per session. If visitors leave too quickly, your content may not be engaging enough.
To reduce bounce rate:
- Improve page speed
- Use engaging, well-structured content
- Add strong calls to action (CTAs)
Local SEO Audit
Google My Business Optimization
If you run a local business, Google My Business (GMB) optimization is crucial. Ensure your GMB profile is:
- Claimed and verified
- Contains accurate business details (name, address, phone number)
- Includes relevant keywords in the business description
- Has positive reviews and high engagement

Local Citations and NAP Consistency
Your business’s Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) must be consistent across all online listings, including Yelp, Bing Places, and social media. Use tools like Moz Local or BrightLocal to check for discrepancies.
Security and Website Health Check
SSL Certificate and HTTPS Implementation
Security is a top-ranking factor. Ensure your website has an SSL certificate (HTTPS) for encryption. Google gives secure websites a ranking boost, and browsers warn users about insecure (HTTP) sites.
Identifying Malware and Security Vulnerabilities
Run security scans using Google Safe Browsing, Sucuri, or Wordfence to detect malware or hacking attempts.
Analyzing Core Web Vitals
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP measures how long it takes for the largest visible content (like an image or heading) to load. Aim for an LCP of under 2.5 seconds.
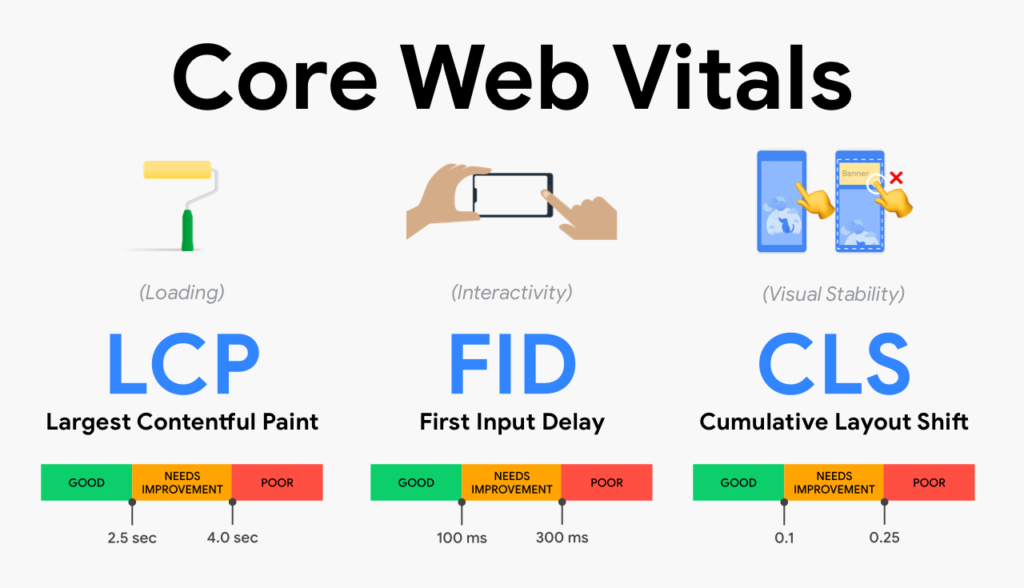
First Input Delay (FID)
FID measures how long it takes for a page to respond to a user’s first interaction (like clicking a button). Keep it under 100 milliseconds for a good experience.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS measures how much content unexpectedly shifts while loading. A CLS score below 0.1 is ideal.
Use Google PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse to analyze and fix Core Web Vitals.
Checking Mobile Usability
Mobile-First Indexing
Since Google primarily indexes mobile versions of websites, your site must be fully optimized for mobile.
Testing with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool
Run your site through Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check if:
- Text is readable without zooming
- Clickable elements aren’t too close together
- Images and videos adjust properly
SEO Audit Report and Action Plan
How to Document Findings
After completing your SEO audit, document the issues you found and categorize them into:
- Critical (Immediate action required) : e.g., site speed issues, broken links
- High Priority (Fix soon) : e.g., missing meta tags, keyword optimization
- Low Priority (Long-term improvements) : e.g., optimizing internal links, adding structured data
Prioritizing Fixes
Address technical and on-page SEO issues first, as they directly impact rankings.
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Over-Optimization
Using too many keywords unnaturally is keyword stuffing and can lead to penalties. Focus on natural, user-friendly content.
Ignoring User Intent
Targeting keywords without understanding search intent can hurt your rankings. Ensure your content matches what users actually want.
Conclusion
SEO audits aren’t a one-time task they should be conducted regularly to maintain strong rankings. By following this guide, you can identify and fix weaknesses, improve your site’s user experience, and ultimately increase organic traffic.
Make SEO audits a routine part of your strategy, and you’ll stay ahead of your competition.
FAQs
1. How often should I conduct an SEO audit?
It’s best to conduct an SEO audit at least every 3-6 months to keep up with algorithm changes and fix technical issues.
2. What is the best free tool for SEO audits?
Google Search Console is one of the best free tools to analyze indexing, errors, and site performance.
3. Can I do an SEO audit myself, or should I hire an expert?
You can perform an SEO audit yourself using tools like Google Analytics, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs, but for in-depth audits, an SEO expert may be beneficial.
4. What are the most critical parts of an SEO audit?
The technical SEO audit, on-page SEO, backlink analysis, and content quality review are the most crucial elements of an SEO audit.
5. Does fixing SEO issues immediately improve rankings?
Some fixes, like site speed improvements and broken link repairs, can lead to quick ranking boosts, but other changes (like backlinks) take longer to impact rankings.